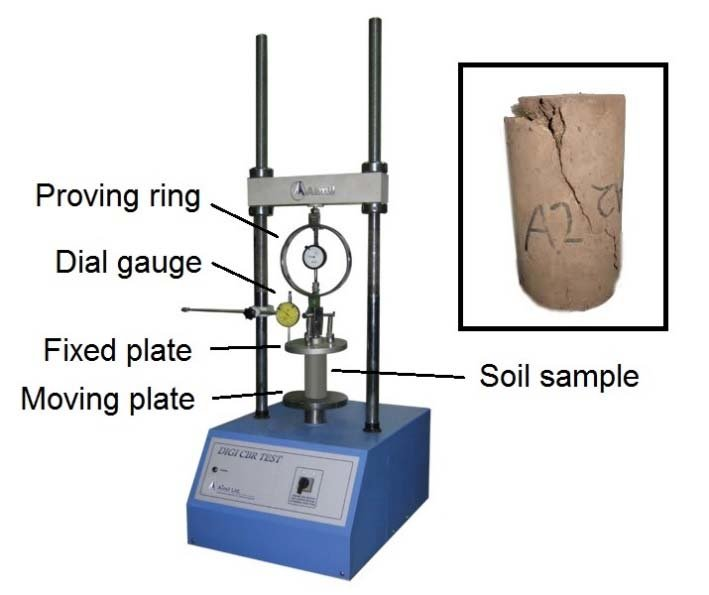
1. Aim:
To determine the California Bearing Ratio of the soil subgrade.
2. Theory:
CBR test originally developed by California Division Highways (USA) is one of the most commonly used methods to evaluate the strength of subgrade soil for design of pavement thickness. CBR value as defined by IS: 2720 (Part XVI)-1979 is the ratio of the force per unit area required to penetrate a soil mass with a circular plunger of 50 mm diameter at the rate of 1.25 mm/minute, to that required for corresponding penetration of a standard material. Standard load ( 1370 kg for 2.5 mm penetration and 2055 kg for 5.0 mm) is the load which has been obtained from tests on a crushed stone whose CBR value is taken to be 100%. The ratio is usually determined for penetration of 2.5 mm and 5.0 mm. The results of this test can be related accurately with fundamental properties of the material but are useful in design of flexible pavements.
3. Apparatus Used:
(a) Mould: A metallic (Gun metal or steel) cylinder of 150 mm internal diameter and 175 mm height; provided with a detachable metal extension collar 50 mm in height. It also has a detachable perforated base plate of 10 mm thickness. The perforation in the base plate do not exceed 1.5 mm in diameter.
(b) Spacer Disc: A metal disc of 148 mm diameter and 47.7 mm in height. The spacer disc has groove on one side so that a handle can be screwed to facilitate its lifting.
(c) Surcharge weight: One annular metal weight and slotted weight of 2.5 kg and 147 mm in diameter with a central hole 53 mm in diameter.
(d) Dial gauges: 2 dial gauges required
(e) IS sieves of size 4.75 mm and 20 mm
(f) Penetration Plunger: A metallic plunger having a diameter of 50 mm and at least 100 mm long.
(g) Loading Machine with a capacity of at least 5000 kg and equipped with a platform that can move vertically @ 1.25 mm/minute.
(h) Proving ring of capacity 5000 kg
(i) Other apparatus like mixing bowl, straight edge, scale, filter paper and measuring jar.
4. Procedure
(i) Sieve the material through 20 mm IS sieve.
(ii) Take about 5.5 kg soil.
(iii) Add water to the soil in the quantity such that the moisture content of the specimen is either equal to field moisture content or OMC desired.
(iv) Mix soil with water uniformly.
(v) Clamp the mould along with the extension collar to the base plate.
(vi) Place the spacer disc in the mould and put a coarse filter paper on top of it. The hole should be on bottom side.
(vii) Pour soil-water mix in the mould in such a quantity the after compaction about 1/3rd (for light compaction) or 1/5th (for heavy compaction) of the mould is filled.
(viii) Give 55 blows with a rammer weighing 2.6 kg, dropping through 310 mm in 3 layers (light compaction) or 4.90 kg, dropping through 450 mm in 5 layers (heavy compaction)
(ix) Scratch the top layer of compacted surface. Add more soil and compact in similar fashion.
(x) Remove the extension collar and trim off the excess soil by a straight edge.
(xi) Remove the base plate, spacer disc and the filter paper and note down the weight of mould and compacted specimen.
4.1. CBR Test on Soaked Specimen:
Prepare the specimen and follow as below:
(i) Weigh the sample excluding base plate and spacer disc.
(ii) Place a filter paper is on the sample with a perforated plate on it.
(iii) Place over it surcharge weight 2.5 to 5.0 kg and soak the sample in water tank for 4 days.
(iv) Allow to drain off water from the sample in a vertical position for 15 minutes.
(v) Weigh the sample again to calculate the percentage of water absorbed.
(vi) Then test the sample following the normal procedure.
5. Testing the Specimen:
(i) Place the mould containing the specimen, with base plate in position, on the testing machine.
(ii) Place the annular weight of 2.5 kg on the top surface of soil.
(iii) Fix the proving ring assembly and penetration plunger on the loading machine
(iv) Bring the penetration plunger in contact with soil surface and apply a seating load of 4 kg so that full contact between soil and plunger is established. This should be taken as zero load.
(v) Place the remaining surcharge weight (slotted weight) so that total surcharge weight equals to 5.0 kg.
(vi) Fix the dial gauge with the tip of its stem resting on the collar to measure the penetration.
(vii) Set the reading of dial gauges to zero.
(viii) Apply load so that penetration rate is 1.25 mm/minute. Record the load at penetration of 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 4, 5, 7.5, 10 and 12.5 mm. In case load reading starts decreasing before 12.5 mm penetration, record the maximum load and the corresponding penetration value.
(ix) Collect about 20 to 50 g soil from the top to determine the water content.
At least 3nspecimens should be tested on each type of sample.
6. Computation of Test Results
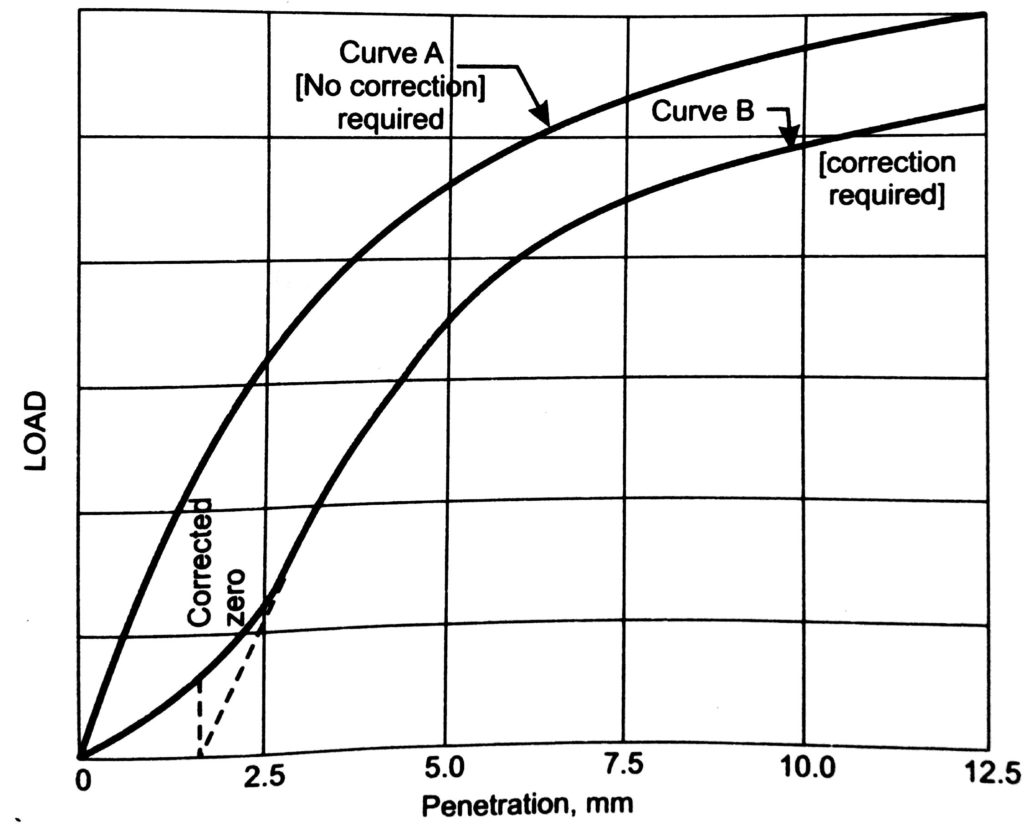
(i) Plot the load penetration curve with load as ordinate and penetration as abscissa. Sometimes the initial portion of the curve is concave upwards due to surface irregularities. In such a case apply a correction. Draw tangent at the point of greatest slope. The point where this tangent meets the abscissa is the corrected zero reading of penetration.
(ii) From the curve, determine the load value corresponding to the penetration value at which the CBR is desired.
(iii) Compute CBR value as follows:
CBR (in %) = Test load corresponding to chosen penetration x 100 / Standard load for the same penetration
Usually CBR value at 2.5 mm penetration will be greater than that at 5.0 mm penetration. Generally the CBR value at 2.5 mm penetration will be greater than that at 5.0 mm penetration and in such a case the former is taken for design purposes. If the 5.0 mm value is greater, the test is repeated. If the same results follow, the CBR value corresponding to 5.0 mm penetration is adopted for design purposes.
Standard Load for different penetration values :
Penetration (in mm) Total Standard Load (kg) Standard Pressure (kg/cm2)
2.5 1370 70
5.0 2055 105
7. Observation:
Type of sample : Undisturbed/ Remoulded
Compaction : Static/ Dynamic
Type of compaction : Light/Heavy
Condition of soaking: Soaked/ Unsoaked
Period of soaking : ----------- hour
Surcharge weight : -------------
Observation Table:
Penetration (mm) No of divisions on proving ring Corresponding load (kg)
0 ------------- ------------
0.5 ------------- -------------
1.0 ------------- -------------
1.5 ------------- -------------
2.0 ------------- -------------
2.5 ------------- -------------
4.0 ------------- -------------
5.0 ------------- -------------
7.5 ------------- -------------
10.0 ------------- -------------
12.5 ------------- -------------
CBR at 2.5 mm penetration = --------------------
CBR at 5 mm penetration = ---------------------------
8. Standard Value:
Soil Type CBR (%)
Well graded gravel (GW) 40-80
Poorly graded gravel (GP) 30-60
Silty Gravel (GM) 40-60
Clayey Gravel (GC) 20-40
Well graded sand (SW) 20-40
Poorly graded sand (SP) 10-40
Silty sand (SM) 10-40
Clayey sand (SC) 5-20
ML or MI <15
CH <15
MH < 10
Organic soil < 5
HAPPY LEARNING
Please follow me on https://talktorashid.blogspot.com/